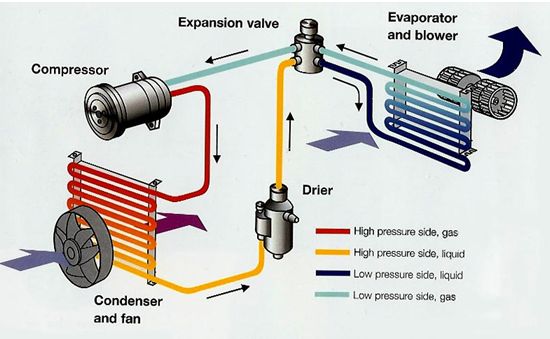
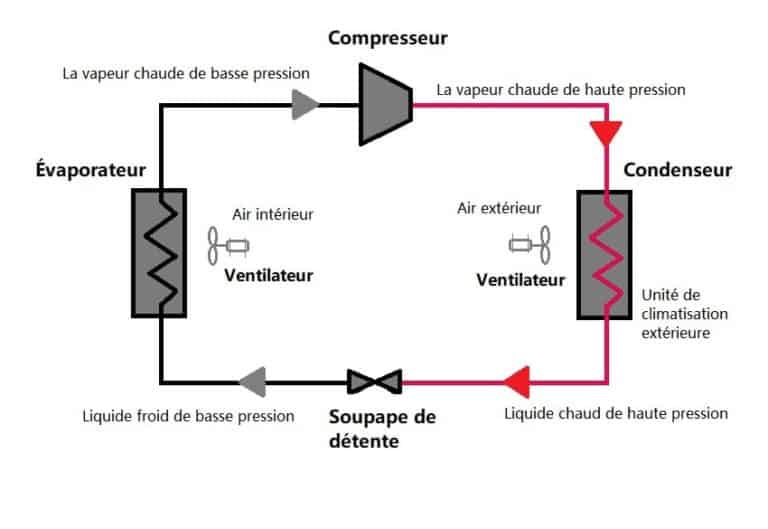
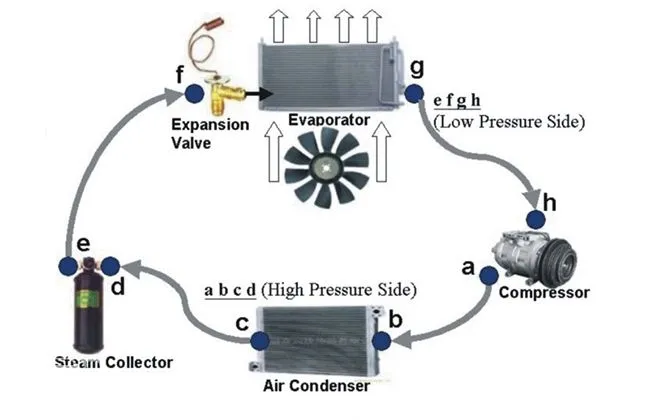
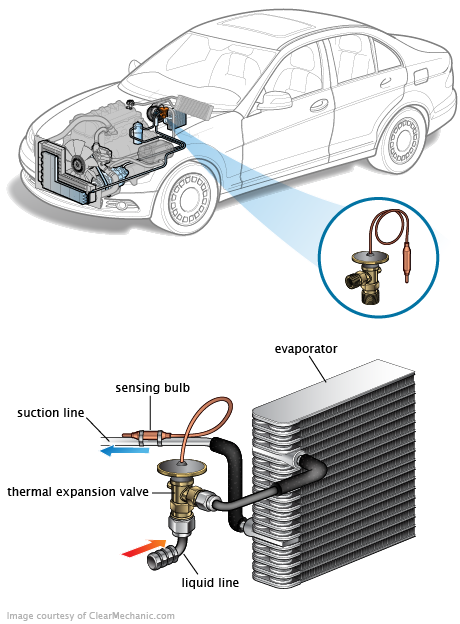
Air Conditioning Evaporator:
The Role of an Air Conditioning Evaporator: An air conditioning evaporator is an essential component of an air conditioning system in automobiles and residential and commercial HVAC systems. Its main role is to cool the air circulating inside a vehicle’s cabin or within a building. Here’s how an air conditioning evaporator works:
Reception of Hot Air: Hot air from the outside or inside the vehicle/building is drawn into the evaporator by a fan. This warm air contains moisture in the form of water vapor.
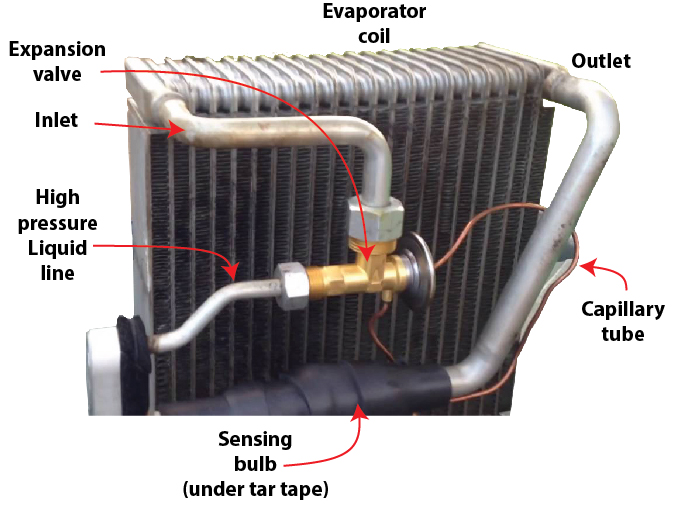
Heat Exchange: The evaporator typically consists of a coil or a set of thin metal tubes. Inside these tubes circulates a refrigerant fluid, often Freon or a similar refrigerant. This fluid is at a very low temperature, well below the ambient air temperature.
Evaporation: The hot air passes over the cold coil or tubes. Due to the temperature difference between the air and the refrigerant inside the tubes, the water in the air begins to condense on the tubes. This condensation forms liquid water vapor.
Cooling of the Air: When water vapor condenses, it releases heat, causing the air circulating around the tubes to cool rapidly. The air exits the evaporator much cooler than when it entered.
Dehumidification: In addition to cooling the air, the evaporator also removes moisture from the air. This occurs because the water vapor in the air condenses on the cold tubes, transforming it into liquid water. This water is then drained out of the air conditioning system.
Distribution of Cooled Air: The cooled and dehumidified air is then distributed into the vehicle’s cabin or indoor spaces of the building through a system of ducts and fans.
The evaporator plays a crucial role in the air cooling and dehumidification process, creating a more comfortable and pleasant indoor environment during hot weather. It’s important to note that the evaporator works in conjunction with other components of the air conditioning system, such as the compressor, condenser, and expansion valve, to maintain the refrigeration cycle necessary for air cooling.
0 commentaire